Procrastination often gets misunderstood as laziness or poor time management, but the truth is much more complex. It is deeply rooted in psychology and driven by fears, subconscious beliefs, and emotional overwhelm. Before you can break free from procrastination, you need to understand why it happens in the first place.
This article explores procrastination’s three primary psychological triggers—fear of failure, perfectionism, and emotional overwhelm—and how our subconscious beliefs shape our tendency to delay essential tasks. Understanding the psychology of procrastination, identifying procrastination triggers, and recognizing the mental blocks behind procrastination are vital for breaking free from avoidance behaviors.
Why Do We Procrastinate?
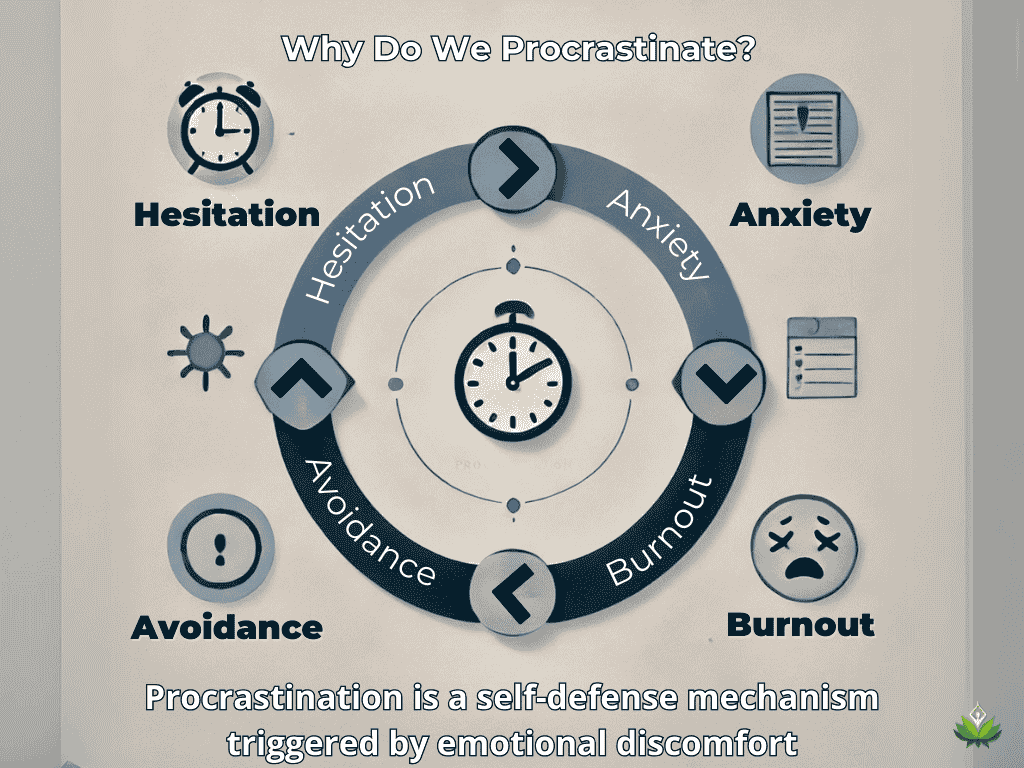
Have you ever planned to start a task but found yourself putting it off despite knowing its importance? This internal battle is not about laziness but how your brain protects you from discomfort. Procrastination is a self-defense mechanism rooted in psychology. It temporarily escapes negative emotions associated with a task, such as fear, stress, or self-doubt.
Procrastination Links to:
- Fear of failure – the anxiety of not meeting expectations.
- Perfectionism – the pressure to produce flawless work.
- Emotional overwhelm – feeling too mentally or emotionally drained to begin.
Understanding why people procrastinate, the psychological triggers of procrastination, and how subconscious beliefs shape it can help us start taking action to overcome it.
1. Fear of Failure: The Paralysis Effect
One of the biggest psychological triggers of procrastination is fear of failure. Many people delay tasks because they worry about not succeeding, making mistakes, or facing criticism. This fear causes a stress response, overwhelming even simple tasks.
How Fear of Failure Creates Procrastination:
- When faced with a task, your brain perceives it as a “threat” to your self-worth.
- Anxiety builds up, and the mind tries to avoid discomfort.
- Instead of starting, you delay—convincing yourself that you’ll do it later when you feel more ready.
Example: A student avoids starting a significant assignment, fearing they won’t do it well enough. Instead of working on it gradually, they put it off until the last minute, increasing their stress levels.
The Role of the Subconscious Mind:
- When people criticize you for childhood mistakes, your subconscious may have connected failure with punishment.
- This fear stays with you into adulthood, making you avoid situations where you might fail.
Recognizing how fear of failure leads to procrastination is crucial for ending the pattern of avoidance.
2. Perfectionism: The Impossible Standard
Perfectionism frequently presents itself as a “desirable quality,” yet it is one of the primary factors contributing to procrastination. Perfectionists set unrealistic expectations for themselves, believing that anything less than perfect is unacceptable. This mindset makes it difficult to start tasks because no effort ever feels “good enough.”
How Perfectionism Leads to Procrastination:
- Instead of making progress, you overthink and over-plan.
- You fear judgment or criticism, which prevents you from taking the first step.
- You convince yourself that starting later will give you more time to perfect the task.
Example: A business owner delays launching a new product because they keep tweaking small details, never feeling “ready.”
The Role of the Subconscious Mind:
- If your subconscious mind equates perfection with worthiness, you will procrastinate on tasks where you fear falling short.
- This results in chronic indecision, missed opportunities, and unfinished projects.
Understanding why perfectionism causes procrastination can help individuals shift their mindset from perfection to progress.
3. Emotional Overwhelm: When Tasks Feel Too Big
Another psychological reason behind procrastination is emotional overwhelm. When a task feels too mentally or emotionally demanding, your brain goes into a “freeze” mode, causing avoidance.
How Emotional Overwhelm Causes Procrastination:
- Your brain sees the task as too much to handle.
- It triggers avoidance, providing temporary relief from stress.
- Postponing a task creates an increased sense of difficulty, which makes starting the work more challenging.
Example: Someone who needs to have a difficult conversation avoids it for weeks because they don’t want to deal with the emotional discomfort.
The Role of the Subconscious Mind:
- If your subconscious mind associates specific tasks with past trauma or negative emotions, you will instinctively avoid them.
- Procrastination, in this case, is a protective mechanism, shielding you from emotional distress.
Recognizing how emotional overwhelm contributes to procrastination can help you regain control over your tasks.
How Subconscious Beliefs Shape Procrastination
Your unconscious mind significantly influences procrastination. Your beliefs about work, success, and failure stem from childhood experiences. Suppose you grew up in an environment where:
- Critics heavily criticized the mistakes → You may fear failure.
- Success was the only thing valued → You may struggle with perfectionism.
- Tasks always felt overwhelming → You may procrastinate due to emotional burnout.
These deep-rooted beliefs create automatic thought patterns that influence your behavior without you realizing it.
Example: If you were frequently told, “You have to be the best,” you might struggle to start tasks because the pressure to be perfect feels unbearable.
One must understand how subconscious beliefs affect procrastination patterns to change behavior effectively.
Being aware marks the beginning of overcoming procrastination habits.
Identifying personal causes behind procrastination represents the essential first step towards overcoming procrastination.
Key Takeaways:
- Procrastination is not about laziness—it is a psychological response to fear, perfectionism, and emotional overwhelm.
- Your subconscious mind exerts a strong influence on the development of procrastination behavior.
- Understanding what causes you to procrastinate will help you develop mental habits.
Reflective Questions:
- At what point did you become preoccupied with postponing work responsibilities?
- What emotion are you trying to escape by procrastinating?
- Do you struggle with perfectionism? How does it impact your work?
- What beliefs about success and failure did you learn in childhood? Are they still serving you?
Procrastination is a complex psychological pattern, but awareness is the first step to change. Once you understand why people procrastinate, how mental blocks behind procrastination form, and how the psychology of procrastination works, you can begin working on the more profound beliefs that keep you stuck.
Look for our upcoming post, which will discuss practical techniques for overcoming procrastination and regaining control of your time and energy!
Angel Dimitrov. (2025). Holistical Method. https://holisticalmethod.com